Difference between revisions of "Microsoft Windows"
(→Vendor IDs) |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 12:48, 16 October 2007
Contents
- 1 Platform Notes
- 2 Version History
- 3 Backoff Patterns
- 4 Vendor IDs
- 5 Authentication Methods
- 6 ISAKMP SA Lifetime
- 7 Transform Ordering and Re-Writing
- 8 Aggressive Mode
- 9 Response to Noncompliant and Malformed Packets
- 10 NAT Traversal
- 11 IVEv2
- 12 Remote Access VPN Client
- 13 Other Interesting Behaviour
- 14 Default Configuration
Platform Notes
Microsoft Windows needs no introduction.
IPsec support was added in Windows 2000. The IPsec implementation claims to be a joint effort between Microsoft and Cisco.
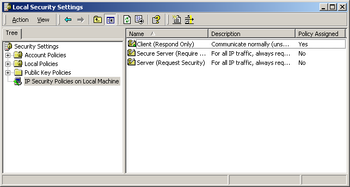
Windows 2000 and higher do not enable IPsec by default. To enable it, an IPsec policy needs to be assigned. This can either be one of the three pre-defined policies, or a custom policy. The screenshot on the right shows the IPsec policies on a Windows 2000 server system with the Client (Respond Only) policy assigned.
There is also a command line configuration tool called Ipsecpol, which is included in the Windows 2000 resource kit.
Version History
| Version | Release Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 2000 | Feb 2000 | First Windows version with IPsec support |
| Windows XP | Oct 2001 | |
| Windows 2003 | Apr 2003 | Added support for Diffie-Hellman group 14 (2048-bit MODP) and NAT Traversal |
| Windows Vista | Jan 2007 | |
| Windows 2008 | ??? 2008 | Currently in beta, codename "Longhorn" |
The Diffie-Hellman group 14 and NAT Traversal support that was added in Windows 2003 is also part of XP SP2. An update is available from Microsoft to add this functionality to Windows 2000 and XP.
Backoff Patterns
All versions of Microsoft windows that support IPsec have the following seven-packet backoff pattern:
0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
Here is the backoff pattern from Windows 2000 Server SP1 on Intel IA-32. This is using Pre-Shared Key authentication, which has been enabled on the server by adding it to the authentication methods for the assigned IPsec policy.
$ ike-scan -M --showbackoff 172.16.3.65
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.3.65 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=64e16a30840b4926)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000002 (Windows-2000)
IKE Backoff Patterns:
IP Address No. Recv time Delta Time
172.16.3.65 1 1171646536.151741 0.000000
172.16.3.65 2 1171646537.155460 1.003719
172.16.3.65 3 1171646539.162840 2.007380
172.16.3.65 4 1171646543.172237 4.009397
172.16.3.65 5 1171646551.175390 8.003153
172.16.3.65 6 1171646567.199850 16.024460
172.16.3.65 7 1171646599.205474 32.005624
172.16.3.65 Implementation guess: Windows 2000, 2003 or XP
Here is the backoff pattern from Windows server 2003 on Intel IA-32:
$ ike-scan -M --showbackoff 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=16b5cca0fcf43a29)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
IKE Backoff Patterns:
IP Address No. Recv time Delta Time
172.16.4.56 1 1171708960.343478 0.000000
172.16.4.56 2 1171708961.008901 0.665423
172.16.4.56 3 1171708963.021053 2.012152
172.16.4.56 4 1171708966.976238 3.955185
172.16.4.56 5 1171708974.987006 8.010768
172.16.4.56 6 1171708991.013191 16.026185
172.16.4.56 7 1171709023.016652 32.003461
172.16.4.56 Implementation guess: Windows 2000, 2003 or XP
Here is the backoff pattern from Windows server 2008 Beta on Intel-IA32:
$ ike-scan -M --showbackoff 192.168.124.168
Starting ike-scan 1.9.1 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.168 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=0f243bdc898d7a4b)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000005 (Windows-Vista)
VID=4a131c81070358455c5728f20e95452f (RFC 3947 NAT-T)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=fb1de3cdf341b7ea16b7e5be0855f120
VID=e3a5966a76379fe707228231e5ce8652
IKE Backoff Patterns:
IP Address No. Recv time Delta Time
192.168.124.168 1 1192538763.047659 0.000000
192.168.124.168 Implementation guess: Linksys Etherfast
Vendor IDs
Microsoft Windows returns the following Vendor IDs:
- Windows Vendor ID (1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e461 plus 4-byte version)
- IKE Fragmentation (4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3) - Windows 2003
- draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n (90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f) - Windows 2003
- (fb1de3cdf341b7ea16b7e5be0855f120) - Windows 2008 server
- (e3a5966a76379fe707228231e5ce8652) - Windows 2008 server
The Windows Vendor ID consists of the 16 bytes of data 1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e461 plus a 4-byte version number in big endian format. The 16 bytes of data is an MD5 hash of the string "MS NT5 ISAKMPOAKLEY". The 4-byte version number identifies the Windows version. The currently known Vendor IDs, and their associated Windows versions are:
| Vendor ID | Windows Version |
|---|---|
| 1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000002 | Windows 2000 |
| 1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000003 | Windows XP or XP SP1 |
| 1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 | Windows XP SP2 or Windows 2003 |
| 1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000005 | Windows Vista or 2008 |
Presumably there was an IPsec version 00000001 before the Windows 2000 release, but I have never observed it. Perhaps it was an internal release for testing, or a beta version.
Authentication Methods
Windows IPsec supports three authentication methods for IKE Phase-1:
- Pre-Shared Key
- RSA Signatures (using X.509 certificates)
- Kerberos V5
The Kerberos V5 authentication method is unique to Windows, and uses the method described in the IETF draft A GSS-API Authentication Method for IKE. Kerberos authentication is only usable if the system is part of a domain (not a workgroup).
By default, the pre-defined policies only allow Kerberos authentication, but Pre-Shared Key and RSA Signature are available as options.
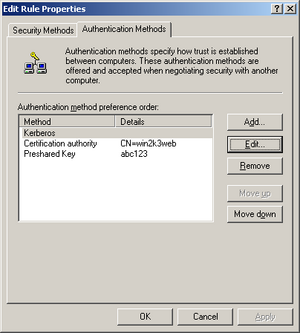
The screenshot on the right shows Windows 2003 with all the possible authentication methods enabled. In this example, Certification authority (meaning RSA signature authentication with an X.509 certificate) and Preshared Key have been manually added to the list of authentication methods.
Below is an example of Kerberos authentication against a Windows XP SP2 system. We need to specify the authentication method 65001, and also specify a GSSID (it doesn't matter what we specify, but we must specify something). The XP system returns a GSSIdentityName attribute in the transform. This is a unicode string, which decodes to roy$@NTA-MONITOR.AD.NTA-MONITOR.COM.
$ ike-scan --gssid=01020304 --trans=5,2,65001,2 -M 192.168.124.11
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.11 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=82ec32b83f4317bd)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=XAUTH LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080
GSSIdentityName(72)=0x72006f007900240040004e00540041002d004d004f004e00490054004f0052002e00410044002e004e00540041002d004d004f004e00490054004f0052002e0043004f004d000000)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
ISAKMP SA Lifetime
All the examples below use Windows 2003 server unless stated otherwise.
No lifetime in seconds or kilobytes is acceptable, and no lifetime attributes are returned in the response.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=none --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=16aa8387a1e4df3b)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
A lifetime in seconds of zero is ignored, and no lifetime attribute is returned in the response.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=0 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=1544071343b34bff)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
The minimum acceptable lifetime in seconds is 60 (one minute).
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=1 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Notify message 14 (NO-PROPOSAL-CHOSEN)
HDR=(CKY-R=6311d130e9e10eaa, msgid=4ae969f5)
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=59 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Notify message 14 (NO-PROPOSAL-CHOSEN)
HDR=(CKY-R=1a13c2ffe2c72fe8, msgid=040c2f07)
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=60 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=f839b51c18d2542d)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x0000003c)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
There is no upper limit to the lifetime in seconds. Here we see the 2003 server accepting the maximum possible 32-bit value.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=0xffffffff --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=cabd91f12cc87976)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0xffffffff)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
But only 32-bit (4-byte) variable-length attributes are supported. Longer attribute lengths are ignored, and shorter ones are mishandled.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=0xffffffffffffffff --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=b925665ed3dedf19)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=0xffff --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56 Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=288afb17ae0a0b7e)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0xffff0000)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
A lifetime in kilobytes of zero is ignored, and not returned in the response.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=none --lifesize=0 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=238bc51a79b1a853)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Any non-zero value for lifetime in kilobytes is accepted and returned.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=none --lifesize=1 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=0825cac2438966aa)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0x00000001)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=none --lifesize=0xffffffff --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=8a4f8670f43fe505)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0xffffffff)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Windows 2003 mis-handles lifetimes in kilobytes with attribute lengths that are not 32-bits.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=none --lifesize=0xff --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=82bd5ce1cae76bc9)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0xff000000)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Both lifetime in seconds and lifetime in kilobytes is also acceptable.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=0xffffffff --lifesize=0xffffffff --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=a553d3394dfdb7d1)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0xffffffff LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0xffffffff)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Transform Ordering and Re-Writing
Windows IPsec always returns transform attributes in the order: Enc, Hash, Group, Auth [,Lifetime in seconds] [,Lifetime in KB] regardless of the initiator attribute ordering.
Variable length attributes are never re-written as basic attributes, and their length is always 4-bytes (32-bits). We have seen in the SA Lifetime section, that Windows does not handle variable length attributes with lengths other than 4-bytes correctly.
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(1=1,2=1,3=1,4=1)" 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=4f0f7ec07c1635ac)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(4=1,3=1,2=1,1=1)" 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=9ee5799aa2fe4df7)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(1=1,2=1,3=1,4=1,11=1,12=123,11=2,12=456)" 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=f1648b494ea2386e)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x0000007b LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0x000001c8)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(11=2,12=456,11=1,12=123,4=1,3=1,2=1,1=1)" 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=d6a7f73061a37a73)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x0000007b LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0x000001c8)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Aggressive Mode
Windows IPsec does not support IKE Aggressive Mode, and it does not respond to aggressive mode requests.
Response to Noncompliant and Malformed Packets
The examples below are all from Windows 2003 unless otherwise noted.
No Acceptable Transforms
$ ike-scan -M --trans=1,2,1,5 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Notify message 14 (NO-PROPOSAL-CHOSEN)
HDR=(CKY-R=029069c09caa43ac, msgid=7268b078)
Bad IKE version
No response from the Windows 2003 server.
Invalid DOI
$ ike-scan -M --doi=2 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Notify message 2 (DOI-NOT-SUPPORTED)
HDR=(CKY-R=f5e1662fa8df0048, msgid=ea0037dd)
Invalid Situation
$ ike-scan -M --situation=2 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Notify message 3 (SITUATION-NOT-SUPPORTED)
HDR=(CKY-R=cfc1f87151331140, msgid=4dfb67ad)
Invalid Initiator Cookie
Windows 2003 does not object to a zero initiator cookie.
$ ike-scan -M --cookie=0000000000000000 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=537b38d2e060c7ef)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Invalid Flags
Windows 2003 does not object to flags=255 (all bits set) in the ISAKMP header.
$ ike-scan -M --hdrflags=255 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56 Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=19ef17781dee8fea)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Invalid Protocol
Windows 2003 does not object to an invalid protocol ID.
$ ike-scan -M --protocol=2 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=4d127014ee92ecea)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Invalid SPI
Windows 2003 does not object.
$ ike-scan -M --spisize=32 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=71107271b9197fe4)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
Non-Zero Reserved Fields
Windows 2003 does not object if the reserved fields are not zero.
$ ike-scan -M --mbz=255 --trans=1,1,1,1 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=411ed03752f3cc56)
SA=(Enc=DES Hash=MD5 Group=1:modp768 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
NAT Traversal
Windows 2003 supports NAT Traversal, although it returns the IETF draft Vendor ID rather than the RFC 3947 one because the RFC was not released until 2005. Below is an example of a Windows 2003 system responding to a NAT Traversal request:
$ ike-scan -M --nat-t 172.16.4.56
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
172.16.4.56 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=a2ca5b1c6389f88f)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007080)
VID=1e2b516905991c7d7c96fcbfb587e46100000004 (Windows-2003-or-XP-SP2)
VID=4048b7d56ebce88525e7de7f00d6c2d3 (IKE Fragmentation)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
IVEv2
Microsoft Windows IPsec does not support IKEv2 as of the Windows 2003 implementation.
Remote Access VPN Client
The Microsoft L2TP/IPSec VPN Client is available for Windows 98, Windows ME and Windows NT 4. From Windows 2000 onwards the VPN client functionality is built into the OS.
Other Interesting Behaviour
Windows sends delete message after timeout
Windows sends an ISAKMP informational message containing a delete payload after it has exhausted its retry sequence. This delete payload is for the ISAKMP SA that was not established, with a 16-byte SPI that consists of the initiator cookie followed by the responder cookie.
Here is an example tcpdump output showing the IKE packets exchanged between ike-scan and a Windows 2000 system. In this example we see the initiator packet followed by six responses with the Windows characteristic backoff timing, and lastly the informational packet (which tcpdump confusingly labels as phase 2/others).
08:25:36.451043 IP 192.168.124.7.500 > 172.16.3.65.500: isakmp: phase 1 I ident 08:25:36.570081 IP 172.16.3.65.500 > 192.168.124.7.500: isakmp: phase 1 R ident 08:25:37.571909 IP 172.16.3.65.500 > 192.168.124.7.500: isakmp: phase 1 R ident 08:25:39.597313 IP 172.16.3.65.500 > 192.168.124.7.500: isakmp: phase 1 R ident 08:25:43.613083 IP 172.16.3.65.500 > 192.168.124.7.500: isakmp: phase 1 R ident 08:25:51.598841 IP 172.16.3.65.500 > 192.168.124.7.500: isakmp: phase 1 R ident 08:26:07.634021 IP 172.16.3.65.500 > 192.168.124.7.500: isakmp: phase 1 R ident 08:26:39.645761 IP 172.16.3.65.500 > 192.168.124.7.500: isakmp: phase 2/others R inf
Here is a hex dump of the IKE delete packet, including the IP and UDP headers:
45 00 00 54 06 e6 00 00 7c 11 4b b2 ac 10 03 41 c0 a8 7c 07 01 f4 01 f4 00 40 89 29 dc 67 f1 19 10 59 7f 23 29 21 1e 27 5d 70 22 c5 0c 10 05 00 cb 64 5f 88 00 00 00 38 00 00 00 1c 00 00 00 01 01 10 00 01 dc 67 f1 19 10 59 7f 23 29 21 1e 27 5d 70 22 c5
Here is a decode of this delete packet:
IP Header 45 00 00 54 06 e6 00 00 7c 11 4b b2 ac 10 03 41 c0 a8 7c 07 UDP Header 01 f4 01 f4 00 40 89 29 ISAKMP Header dc 67 f1 19 10 59 7f 23 initiator cookie 29 21 1e 27 5d 70 22 c5 responder cookie 0c next = 12 (Delete) 10 version = 1.0 05 exchange type = 5 (Informational) 00 flags = 0 cb 64 5f 88 message id 00 00 00 38 length = 56 bytes Delete Payload 00 next = 0 (None) 00 reserved 00 1c length = 28 bytes 00 00 00 01 DOI = 1 (IPsec) 01 protocol id = 1 10 spi size = 16 bytes 00 01 no. of SPIs = 1 dc 67 f1 19 10 59 7f 23 29 21 1e 27 5d 70 22 c5 SPI
Default Configuration
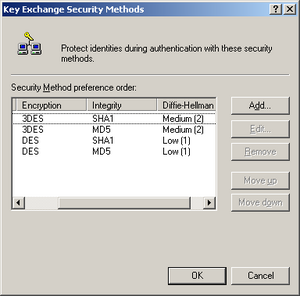
The Windows 2000 default IKE Phase-1 transform attributes are shown in the screenshot on the right. These settings control which transform attributes Windows 2000 will accept when it is acting as a responder. The default setting corresponds to (3DES and (SHA1 or MD5) and DH Group 2) or (DES and (SHA1 or MD5) and DH Group 1).
Windows 2003 has the same default transform attribute support. Although Windows 2003 supports Diffie-Hellman group 14 (2048-bit), this is not enabled by default.
The AES encryption algorithm is not supported in either Windows 2000 or Windows 2003, and neither is Diffie-Hellman group 5.