Difference between revisions of "Juniper NetScreen"
(→Version History) |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 09:31, 27 October 2013
Contents
- 1 Platform Notes
- 2 Version History
- 3 Backoff Patterns
- 4 Vendor IDs
- 5 Authentication Methods
- 6 ISAKMP SA Lifetime
- 7 Transform Ordering and Re-Writing
- 8 Aggressive Mode
- 9 Response to Noncompliant and Malformed Packets
- 10 NAT Traversal
- 11 IVEv2
- 12 Remote Access VPN Client
- 13 Other Interesting Behaviour
- 14 Default Configuration
Platform Notes
Juniper NetScreen is a Firewall/VPN system that runs on proprietary hardware using a proprietary operating system called ScreenOS.
It supports both site-to-site and remote access VPNs.
It uses a Motorola CPU and a Gigascreen ASIC. In an NS-5XP (which is now an obsolete model) the CPU is labelled XPC850DEZT50BT/OK29A/KOREA/ZQQVL0040 and the ASIC is labeled 240E2A01TBB1/JAPAN 0225HAL/L65093.
Version History
| Version | Release Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0.0 | ||
| 4.0.1 | ||
| 4.0.2 | ||
| 4.0.3 | ||
| 5.0.0 | ||
| 5.1.0 | ||
| 5.2.0 | May 2005 | |
| 5.3.0 | June 2006 | DPD support added in 5.3.0r2 |
| 5.4.0 | October 2006 |
Most NetScreen devices run either 5.x or 6.x version code.
Backoff Patterns
The NetScreen has the 12-packet backoff pattern:
0, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4
Here is an example using Main Mode with the default transform set against an NS5-GT running ScreenOS 5.4.0:
$ ike-scan --showbackoff -M 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=324e3633e6174897)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=28800)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
IKE Backoff Patterns:
IP Address No. Recv time Delta Time
192.168.124.155 1 1170083575.291442 0.000000
192.168.124.155 2 1170083578.843019 3.551577
192.168.124.155 3 1170083582.842737 3.999718
192.168.124.155 4 1170083586.843883 4.001146
192.168.124.155 5 1170083590.843073 3.999190
192.168.124.155 6 1170083594.842743 3.999670
192.168.124.155 7 1170083598.843378 4.000635
192.168.124.155 8 1170083602.843049 3.999671
192.168.124.155 9 1170083606.843363 4.000314
192.168.124.155 10 1170083610.843924 4.000561
192.168.124.155 11 1170083614.843497 3.999573
192.168.124.155 12 1170083618.843629 4.000132
192.168.124.155 Implementation guess: Juniper-Netscreen
Vendor IDs
NetScreen's return some or all of the following Vendor IDs in both Main and Aggressive Mode:
- Heatbeat Notify (4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100)
- NetScreen Vendor ID (data varies - see below)
- Dead Peer Detection (afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100) - ScreenOS 5.3.0r2 and later.
- draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02 (90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f) - If NAT Traversal is enabled.
- draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00 (4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc) - If NAT Traversal is enabled.
The NetScreen Vendor ID varies with different versions of ScreenOS and different hardware models. It consists of 20-bytes of data with no obvious structure (probably an SHA1 hash) followed by eight bytes, which appears to consist of two big endian 4-byte (32-bit) values. It is not known what the first of these values represents, but the second 4-byte value appears to indicate the ScreenOS version number for some ScreenOS versions, e.g. "403" for 4.0.3 and "500" for 5.0.0.
Below are some examples of NetScreen Vendor IDs together with the corresponding hardware platform and ScreenOS version.
| Vendor ID | Hardware | ScreenOS |
|---|---|---|
| 64405f46f03b7660a23be116a1975058e69e83870000000400000403 | ns5xp | 4.0.3r3.0 |
| 299ee8289f40a8973bc78687e2e7226b532c3b760000000900000500 | ns5xp | 5.0.0r1.0 |
| 299ee8289f40a8973bc78687e2e7226b532c3b760000000900000500 | ns5xp | 5.0.0r6.0 |
| 299ee8289f40a8973bc78687e2e7226b532c3b760000000900000500 | ns5xp | 5.0.0r9.0 |
| 4a4340b543e02b84c88a8b96a8af9ebe77d9accc0000000b00000500 | ns5gt | 5.0.0r7.1 |
| 2a2bcac19b8e91b426107807e02e7249569d6fd30000000b0000050a | ns5gt | 5.1.0r1.0 |
| 166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 | ns5gt | 5.2.0r3b.0 |
| 166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 | ns5gt | 5.3.0r4.0 |
| 166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 | ns5gt | 5.4.0r1.0 |
| 71957fc3620a421970709668132e871a332378fc0000000b00000614 | ns5gt | 6.2.0r18.0 |
Authentication Methods
NetScreen supports Pre-Shared key (PSK) and RSA Certificate authentication for IKE Phase-1. It also supports XAUTH as an optional additional authentication step between Phase-1 and Phase-2.
ISAKMP SA Lifetime
NetScreen running ScreenOS 5.4.0 supports life types of both seconds and kilobytes. It supports values from 1 to 0xffffffff for either life type, but ignores zero and value lengths greater than four bytes.
It will re-write variable-length lifetime attributes where the life type is seconds and the value is less than 32,767. The example below shows this attribute re-writing.
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=32766 --trans=5,2,1,2 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=83e7dc8ed57dd340)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=32766)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
$ ike-scan -M --lifetime=32767 --trans=5,2,1,2 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=3b81818b8a338825)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration(4)=0x00007fff)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
Transform Ordering and Re-Writing
NetScreen always returns the transform attributes in the order: Enc, Hash, Group, Auth [,keylength] [,lifetime in seconds] [,lifetime in kb] regardless of the order that the attributes are sent by the initiator. The examples below demonstrate this behaviour.
In the example below we send a single transform with the attributes Enc=3DES, Hash=SHA1, Auth=PSK, DH Group=2, and we observe the attribute ordering in the response to be Enc, Hash, DH Group, Auth.
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(1=5,2=2,3=1,4=2)" 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=3c966f12554558de)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
In this example, we use the same attributes as in the example above but reverse their order so that it is now DH Group, Auth, Hash, Enc. We see that the attribute ordering in the response is the same as for the first example: Enc, Hash, DH Group, Auth.
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(4=2,3=1,2=2,1=5)" 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=8fbc70868b6ff405)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
Here is an example including SA lifetime attributes. The initiator attributes are: LifeType=KB, LifeTime=123, LifeType=Seconds, LifeTime=456, DH Group=2, Auth=PSK, Hash=SHA1, Enc=3DES. The responder returns the attributes in order: Enc, Hash, DH Group, Auth, LifeType=Seconds, LifeTime, LifeType=KB, LifeTime.
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(11=2,12=123,11=1,12=456,4=2,3=1,2=2,1=5)" 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=94184ccac11162ee)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=456 LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0x0000007b)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
This example uses the variable key length AES encryption algorithm, and adds the keylength attribute. Otherwise the attributes are the same as the previous example.
$ ike-scan -M --trans="(14=128,11=2,12=123,11=1,12=456,4=2,3=1,2=2,1=7)" 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=b973f6e997f0185e)
SA=(Enc=AES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK KeyLength=128 LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=456 LifeType=Kilobytes LifeDuration(4)=0x0000007b)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
Aggressive Mode
NetScreen supports IKE Aggressive Mode in addition to Main Mode. However you need to specify a valid ID to elicit a response; if you don't specify a valid ID, then the NetScreen won't respond. This introduces a username enumeration vulnerability, because it is possible to determine if a given username exists.
The netscreen accepts the default ID type of 3 (ID_USER_FQDN), so there is no need to explicitly specify this with --idtype.
Below is an example aggressive mode response from a NetScreen 5GT running ScreenOS 5.4.0, using the valid ID royhills@hotmail.com. We also capture the parameters required to crack the pre-shared key with --pskcrack and use psk-crack to obtain the key.
$ ike-scan -A -M --id=royhills@hotmail.com --pskcrack=netscreen.psk 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Aggressive Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=c09155529199f8a5)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=28800)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
KeyExchange(128 bytes)
Nonce(20 bytes)
ID(Type=ID_IPV4_ADDR, Value=192.168.124.155)
Hash(20 bytes)
$ psk-crack netscreen.psk Starting psk-crack [ike-scan 1.9] (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/) Running in dictionary cracking mode key "abc123" matches SHA1 hash 70263a01cba79f34fa5c52589dc4a123cbfe24d4 Ending psk-crack: 10615 iterations in 0.166 seconds (63810.86 iterations/sec)
Response to Noncompliant and Malformed Packets
The NetScreen has three types of responses to noncompliant or malformed packets:
- For some, it returns an Informational IKE exchange with a Notify payload;
- For some, it does not respond at all; and
- It totally ignores some, responding as it would without the offending bit.
The examples below are all from a Netscreen 5-GT running ScreenOS 5.4.0.
No Acceptable Transforms
$ ike-scan -M --trans=1,1,1,1 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Notify message 14 (NO-PROPOSAL-CHOSEN)
HDR=(CKY-R=2c8783fe8032dd4d)
Bad IKE version
$ ike-scan -M --headerver=0x30 192.168.124.155 Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/) $ ike-scan -M --headerver=0x15 192.168.124.155 Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
No response.
Invalid DOI
$ ike-scan -M --doi=2 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Notify message 2 (DOI-NOT-SUPPORTED)
HDR=(CKY-R=a969e6169d9cb489)
Invalid Situation
$ ike-scan -M --situation=2 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=871bd8a5a746467a)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=28800)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
The invalid situation is ignored.
Invalid Initiator Cookie
$ ike-scan -M --cookie=0000000000000000 192.168.124.155 Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
No response.
Invalid Flags
$ ike-scan -M --hdrflags=255 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=292cc88897b534ac)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=28800)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
The invalid header flags are ignored.
Invalid Protocol
$ ike-scan -M --protocol=2 192.168.124.155 Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
No response.
Invalid SPI
$ ike-scan -M --spisize=32 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=33dfbc4d41df9ddb)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=28800)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
The SPI is ignored.
Non-Zero Reserved Fields
$ ike-scan -M --mbz=255 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=b0c2fc28608ab2fe)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=28800)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
The non-zero reserved fields are ignored.
NAT Traversal
NetScreen does not support NAT Traversal by default, but it can be enabled with the following command line configuration option:
set ike gateway "<gateway-name>" nat-traversal keepalive-frequency 0
or by checking the Enable NAT-Traversal box in the GUI under VPNs > AutoKey Advanced > Gateway > Edit > Advanced.
Below is an example of a NetScreen 5GT running ScreenOS 5.4.0. Notice the two additional Vendor IDs that are returned when NAT Traversal is enabled.
$ ike-scan -M --nat-t 192.168.124.155
Starting ike-scan 1.9 with 1 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/ike-scan/)
192.168.124.155 Main Mode Handshake returned
HDR=(CKY-R=35d449a0fa2e4aec)
SA=(Enc=3DES Hash=SHA1 Group=2:modp1024 Auth=PSK LifeType=Seconds LifeDuration=28800)
VID=166f932d55eb64d8e4df4fd37e2313f0d0fd84510000000000000000 (Netscreen-15)
VID=90cb80913ebb696e086381b5ec427b1f (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n)
VID=4485152d18b6bbcd0be8a8469579ddcc (draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-00)
VID=afcad71368a1f1c96b8696fc77570100 (Dead Peer Detection v1.0)
VID=4865617274426561745f4e6f74696679386b0100 (Heartbeat Notify)
IVEv2
Juniper NetScreen supports IKEv2 from ScreenOS 6.1.0.
Remote Access VPN Client
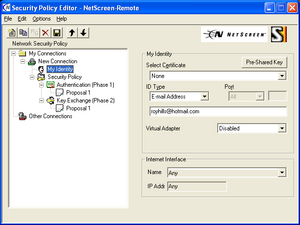
Juniper NetScreen uses NetScreen-Remote, which is a badged version of the SafeNet SoftRemote product that is also used by many other vendors.
It supports both Pre-Shared Key (PSK) and RSA Signature authentication. In both cases, it can also perform XAUTH authentication after the initial Phase-1 authentication has completed.
The IKE Phase-1 proposal contains a single transform. The default transform attributes are:
| No. | Encryption | Hash | Authentication | DH Group | Lifetime (Seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3DES | SHA1 | PSK or RSA | 2 (MODP 1024) | Unspecified |
The transform will use either PSK or RSA authentication based on the authentication method that is selected in the Identity configuration.
The transform attributes can be changed by the user, and the following values are available:
| Encryption | DES, Triple-DES, AES-128, AES-192 or AES-256 |
|---|---|
| Hash | MD5 or SHA1 |
| Authentication | RSA Signature or Hybrid |
| DH Group | 1, 2 or 5 |
Other Interesting Behaviour
Default Configuration
The NetScreen IKE Phase-1 transform attributes are set in the ike gateway configuration. In the GUI, this is under VPNs > AutoKey Advanced > Gateway. The transform set is defined by the security level setting. There are four defined security levels:
- standard - The default security level setting
- compatible
- basic
- custom - User-defined transform set.
Below is an example configuration file entry which defines the IKE gateway test_gw with security level standard:
set ike gateway "test_gw" address 0.0.0.0 id "royhills@hotmail.com" Main outgoing-interface "trust" preshare "zORvTgiuNxaV6RsEHMCQnEZ0cKn5L8mNgQ==" sec-level standard
The example has been wrapped across two lines for readability, but in the configuration it would be on a single line.
The default standard security level supports the following transform attributes:
| Encryption | 3DES or AES/128 |
|---|---|
| Hash | SHA1 |
| Authentication | Pre-Shared Key |
| DH Group | 2 (MODP 1024) |